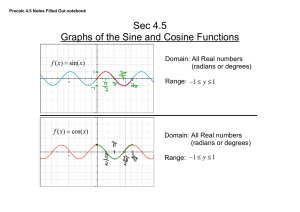
Sec 4.5 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Domain: All Real numbers (radians or degrees)
advertisement
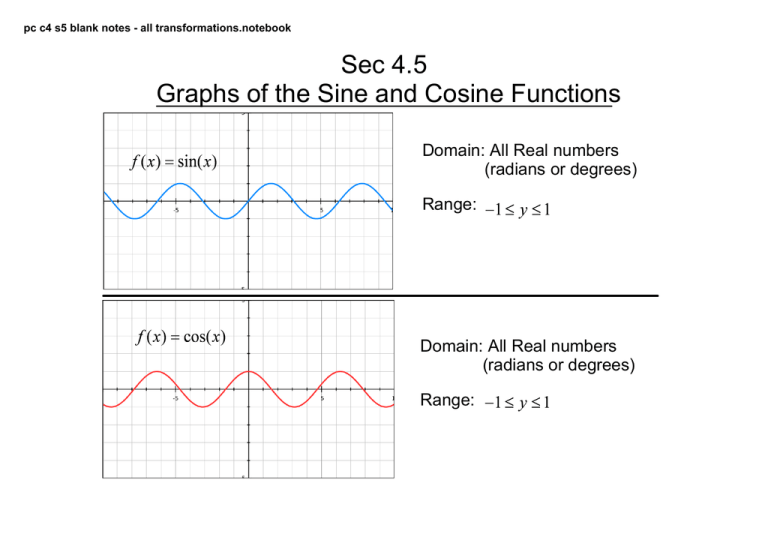
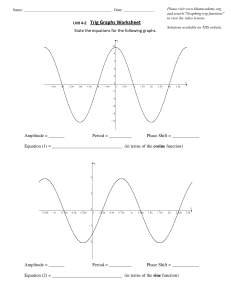
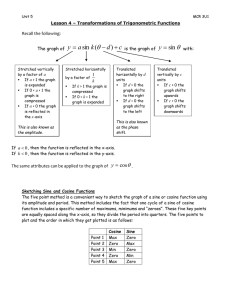
pc c4 s5 blank notes ­ all transformations.notebook Sec 4.5 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Domain: All Real numbers (radians or degrees) Range: Domain: All Real numbers (radians or degrees) Range: pc c4 s5 blank notes ­ all transformations.notebook Characteristics of Trig Functions ­ all trig functions repeat themselves, the horizontal distance it takes for the graph to repeat itself is called the period. ­ the sine and cosine functions have an amplitude. It is defined as half the distance between the maximum and minimum values. For the basic sine function period = amplitude = For the basic cosine function period = amplitude = pc c4 s5 blank notes ­ all transformations.notebook Transformations amplitude = phase shift = period d = vertical shift bx ­ c : shift right positive : shift up bx + c : shift left negative : shift down the left and right endpoints of a one­cycle interval can be found by solving the two equations: left endpoint: bx ­ c = 0 right endpoint: bx ­ c = 2 pc c4 s5 blank notes ­ all transformations.notebook Example Identify the amplitude,period, phase shift, and vertical shift amplitude period phase shift A) B) C) Example Identify the amplitude,period, phase shift, and vertical shift. Then graph. vertical shift pc c4 s5 blank notes ­ all transformations.notebook Example Identify the amplitude and period from the equations The sine & cosine graphs can be changed to any size wave by changing some things in the equation. ­ these variables do the same thing to the sine and cosine graphs d = vertical shift